Phishing Attacks: Part 1
What is Phishing?
Phishing attacks use e-mail to trick users into downloading malware onto their systems for the purpose of stealing information or placing the user in a compromising position that the attacker can exploit.
Malware can be ransomware, which encrypts all files until the victim pays a ransom – usually in bitcoin or other untraceable monetary medium. It can also be a keylogger, which sends all keystrokes back to the attacker. This includes usernames and passwords to bank accounts, credit cards, and other financial or health portals. Malware can also remotely turn on your cameras and microphones to secretly record a user, hoping to record a conversation or video that they wish to keep private.
Are You Being Phished?
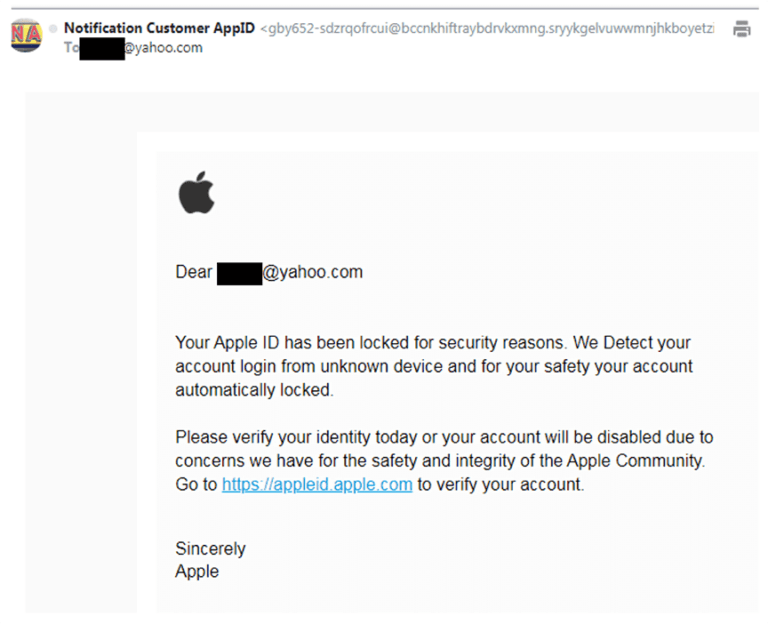
Phishing attacks have become increasingly sophisticated; however, some are easy to spot, like the example below. Now I, along with several billions users, have had my Yahoo account compromised. Thus, the fact that someone has my user name is not a surprise.
Oh no! My Apple account has been locked for my own security. I need to click the link immediately!
Except that I don’t have an Apple ID account. So why I am getting this message?
How to Detect a Phishing Attack
Let’s examine this e-mail closer. First, the subject is a response; however, I never initiated a conversation. If this was a real alert, then Apple or their monitoring service would have started the conversation. There would be no “Re:” in the subject.
Now let’s click on the sender logo. What – no Apple logo?
Then look at the return address! Just a bunch of characters and numbers – no Apple ID anywhere.
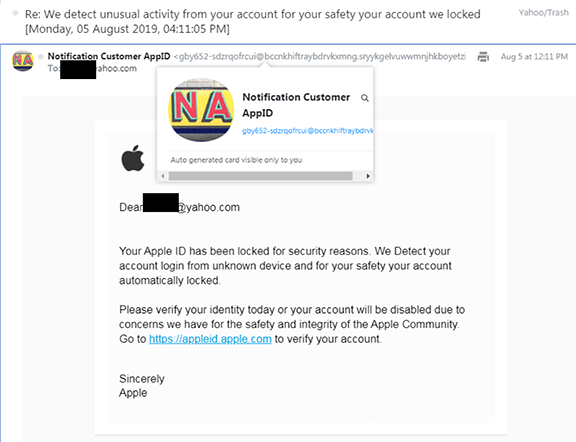
Next, look at the origination address in the e-mail. Again, only letters and numbers. Surely, responding to an Apple alert should send e-mail to someone at Apple.
Now, look at the message. Clearly, the attacker is from a foreign country or else English is not a native language. They use language such as “from unknown device” instead of “from an unknown device.” Also, why is “Detect” capitalized?
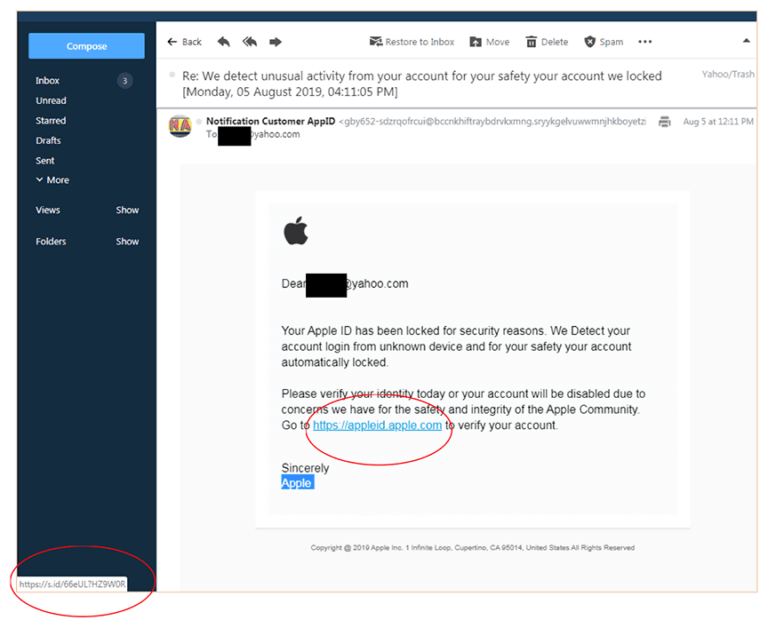
Finally, hover over the link the attacker wants to you click and see where the e-mail is going. That’s not an Apple address! That’s just another series of numbers and letters.
Tips and Tricks to Avoid Phishing Scams
This is not a very sophisticated phishing attack. There are some attacks that fool even seasoned cyber security professionals. Fortunately, there are several rules to follow that everyone should take to protect themselves.
- Never click on a link in a suspicious e-mail.
- If you are informed that an account of yours has been compromised, call the number on the back of the charge card, or log into your account. Never call the number provided in the e-mail. These are phony numbers answered by the scammers that sent out the e-mail.
- After you confirmed the e-mail was bogus, delete the e-mail, and then delete the e-mail from the trash folder.
- If you receive a message from a trusted source (friend, co-worker, relative) asking you to do something out of the ordinary, contact that person. It is likely that person’s e-mail account has been compromised.
Remember: an attacker can send out millions of e-mails with one click. If less than 1% of the people perform a foolish act, the attack is still very profitable. Don’t be part of the 1%.
Why Choose ASCERTIS Solutions
ASCERTIS Solutions can conduct a security assessment of a small business in a week and provide a roadmap for your company to implement a cyber defense strategy that fits your budget. Trained security professionals can be hired on a part-time basis to fill the role of Chief Cyber Security Officer (CISO) to assure that your roadmap is implemented in a timely and cost-effective fashion.
If interested, please contact assessments@ascertis.solutions.
